- HOME
- Enterprise
- Key Capabilities for Future-Proofing Enterprise Billing Systems
Key Capabilities for Future-Proofing Enterprise Billing Systems
Introduction
Generic and legacy billing systems are inherently tied to very specific use cases. As businesses outgrow their typical AR processes, they will start to notice inefficiencies in their billing systems. However, switching billing systems should not be a decision made in haste. It is critical for enterprises to ask important questions that help identify gaps in billing systems before taking the plunge.

With the challenges of existing billing stacks addressed, let's discuss setting realistic expectations from billing software, namely the core capabilities to look for when evaluating an enterprise billing system.
Key capabilities of a robust billing system
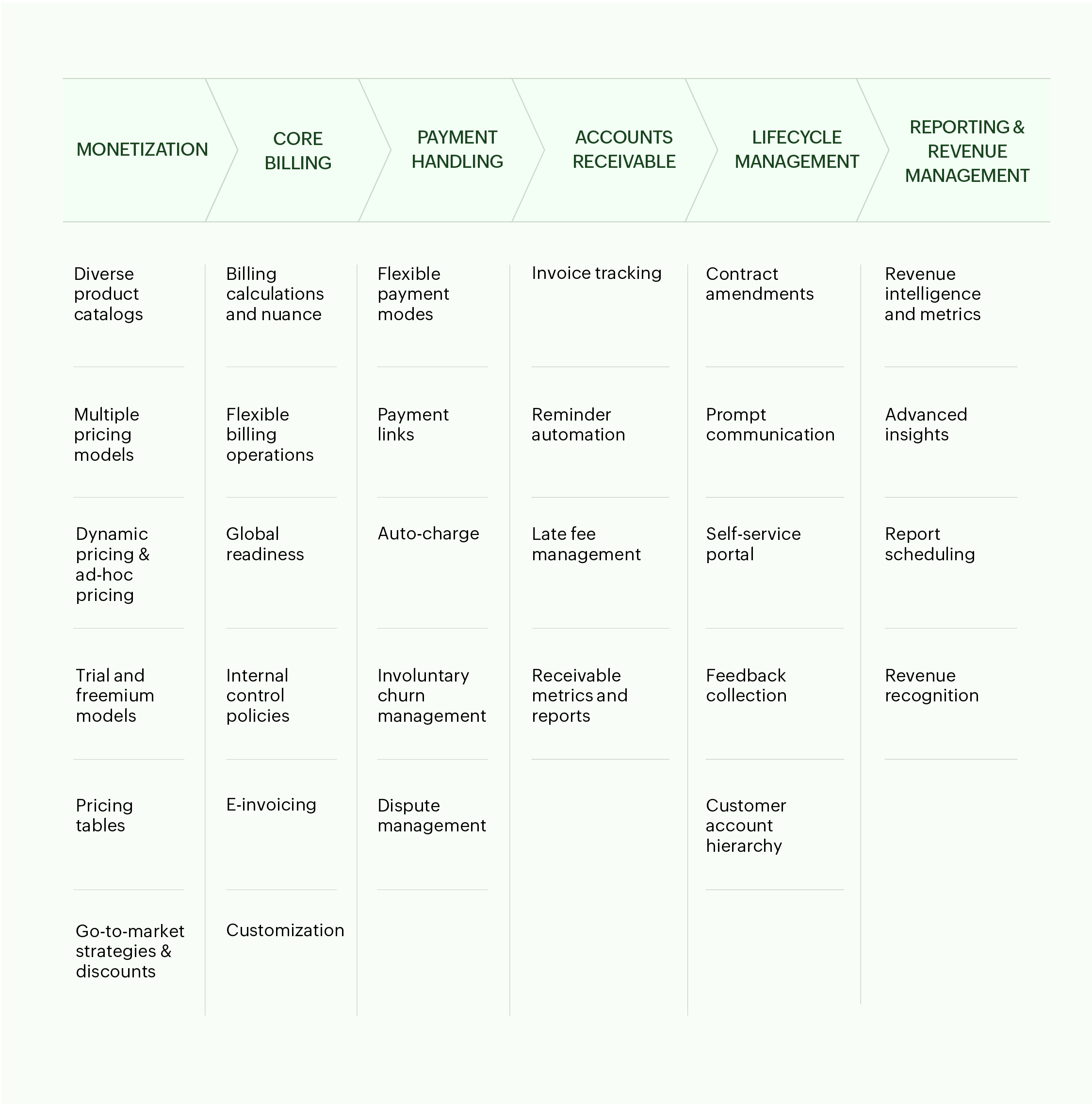
1. Monetization
To adapt to evolving customer needs and modern revenue strategies, billing systems should support:
Diverse product catalogs that cater to current product lines and any future diversification that the enterprise might iterate on, including one-time goods and services, subscriptions, and a hybrid mix.
Multiple pricing models that give teams more control over how products are packaged and monetized. This includes support for flat-rate, volume-based, tiered, and hourly pricing, as well as usage-based billing and retainer models.
Dynamic pricing and ad-hoc pricing like region-specific pricing, surge/demand-based pricing, seasonal adjustments, and preferential pricing without manual workarounds.
Trial and freemium models that can be customized and extended as needed, giving sales teams time to identify and convert hot leads.
Pricing tables that can be embedded into websites and product pages directly. It significantly reduces development overhead while empowering customers to self-checkout easily.
Go-to-market strategies and discounts that enable product, marketing, and sales teams to run limited-time offers, pricing experiments, and discount campaigns.
2. Core billing
Enterprises should adopt billing systems to handle:
Billing calculations and nuances like proration, set up fees, taxes and miscellaneous charges, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and operational efficiency across finance teams.
Flexible billing operations that cater to various cadences, including partial, progressive, and advance invoicing, consolidated invoicing, backdated subscriptions, and invoicing based on anniversary or calendar dates.
Global readiness, including capabilities to handle invoices in customers' local currencies and taxes, in their preferred regional languages.
Internal control policies through multi-level approval workflows for quotes, invoices, discounts, and other transactions while allowing role-based restrictions for improved governance.
E-invoicing obligations natively like automating e-invoice creation, validation, and e-signature protocols.
Customization of the invoice's structure, design, and data fields. It should also allow configuring multiple templates to cater to customers of different segments.
3. Payment handling
Opt for billing software that aligns with the enterprise's payment handling needs and offers:
Flexible payment modes including credit and debit cards, bank transfers, digital wallets, and region-specific options like ACH, Direct Debit, UPI, Alipay, Apple Pay, and M-PESA.
Payment links that allow sales teams to collect payments from customers directly without invoices or emails.
Auto-charge to automatically collect subscription renewal fees from customers' bank accounts using saved payment methods.
Involuntary churn management through built-in retry logic, proactive alerts, and automatic status updates to recover lost payments and mitigate churn.
Dispute management to manage events like chargebacks and refunds that occur due to billing and delivery errors.
4. Accounts receivable
Consider implementing billing systems that empower AR teams with out-of-the-box collection capabilities like:
Invoice tracking to automatically update invoice payment statuses—sent, viewed, outstanding, overdue, partially, and fully paid.
Reminder automation with configurable reminder algorithms, email customization and scheduling, and escalation mechanisms for overdue payments.
Late fee management that enforces penalties like minimum, flat, and percentage-based rates. This incentivizes defaulters to make faster payments, reducing the need for manual follow-ups.
Receivable metrics and reports to speed up collections—including Day Sales Outstanding (DSO), outstanding payments, and aging reports.
5. Lifecycle management
Provide frictionless experiences by putting customers in the forefront using a billing system that offers:
Contract amendments to handle instances like reactivations, cancellations, upgrades, downgrades, pauses, and subscription resuming.
Prompt communication to keep customers informed of key events like extended trials, successful payments, and renewed subscriptions.
Self-service portal that empowers customers to view past transactions, download statements, update addresses, and save payment details without reaching out to support teams.
Feedback collection to leverage timely ratings and reviews, giving product teams actionable inputs to refine offerings and address gaps.
Customer account hierarchy to establish parent-child relationships between branches of the same organization to segment transactions, sales ownership, and reports.
6. Reporting and revenue recognition
Choose billing systems that empower CXOs to make smart business decisions through:
Revenue intelligence and metrics that offer visibility into business KPIs to uncover activations, churn patterns, and sales numbers.
Advanced insights that offer in-depth drill-down reports to discover top-selling products, make revenue projections, and understand behavioral patterns using cohort analysis charts.
Report scheduling to deliver financial reports to key stakeholders and leadership teams based on predefined frequencies like weekly or biannually.
Revenue recognition to ensure adherence to global accounting standards like ASC 606 and IFRS 15 through flexible, rule-based revenue allocation.
Discover Zoho Billing—the monetization platform that drives enterprise growth
Zoho Billing is an enterprise-grade monetization platform built to handle the evolving billing needs of businesses. The platform's enterprise-readiness comes from first-hand experience. As the billing backbone of Zoho's 130+ million users, Zoho Billing has evolved with unique, real-world monetization use cases. From supporting multiple pricing strategies and complex billing cycles to automating compliance and revenue intelligence, Zoho Billing is ideal for scaling enterprises looking to expand markets and drive sustained growth.
After quick deployment and implementation cycles, Zoho Billing empowers sales teams to offer custom bundles and close deals. AR teams are equipped with the right tools to reduce DSO; finance gains accuracy with automated revenue recognition. IT teams aren't scrambling to keep systems up to date, and leadership teams have critical reports at their disposal to make strategic, data-driven business decisions. It offers all of this without the sky-high prices that are typically associated with enterprise billing systems.
With all the right components of an enterprise-grade billing system working smoothly, teams within organizations are in sync, accelerating towards hypergrowth, and focused on driving innovation.
Conclusion
It's important to critically evaluate if your systems are well-equipped to support versatile monetization methods and act as a growth engine for your enterprise. If billing is seen as an obstacle to your enterprise's agile strategies, it's time to consider alternatives.
With this evaluation framework, enterprises can assess gaps in existing infrastructure that can be bridged with modern, agile monetization solutions. The right billing solution should help enterprises future-proof themselves, allowing space for unlocking new revenue opportunities and scaling with confidence.
