- HOME
- Payroll administration
- HRA full form, calculation in salary, and exemption rules
HRA full form, calculation in salary, and exemption rules
House Rent Allowance (HRA) is an essential part of employee compensation and has a direct impact on a company's payroll and employees' tax liabilities. HRA calculations must be accurate and in line with tax regulations set by the government.
This guide will help you understand what HRA is, how to correctly calculate HRA for employees, and HRA exemption rules.

HRA full form
The full form of HRA is House Rent Allowance. This salary component is a type of allowance provided by employers to employees to help cover the rental accommodation expenses they incur.
The amount of HRA is influenced by factors such as the employee's salary, the city they reside in, and the company’s salary structure. Employees living in metro cities typically receive higher allowances due to the higher cost of living compared to those in non-metro areas.
HRA calculation formula
HRA can be calculated either as a fixed amount or as a percentage of the employee’s basic salary.
- For HRA calculation as a percentage of the basic salary:
HRA = Percentage mentioned in the employment contract * Basic salary
- For HRA calculated as a fixed amount:
HRA = Fixed amount of CTC mentioned in the employment contract
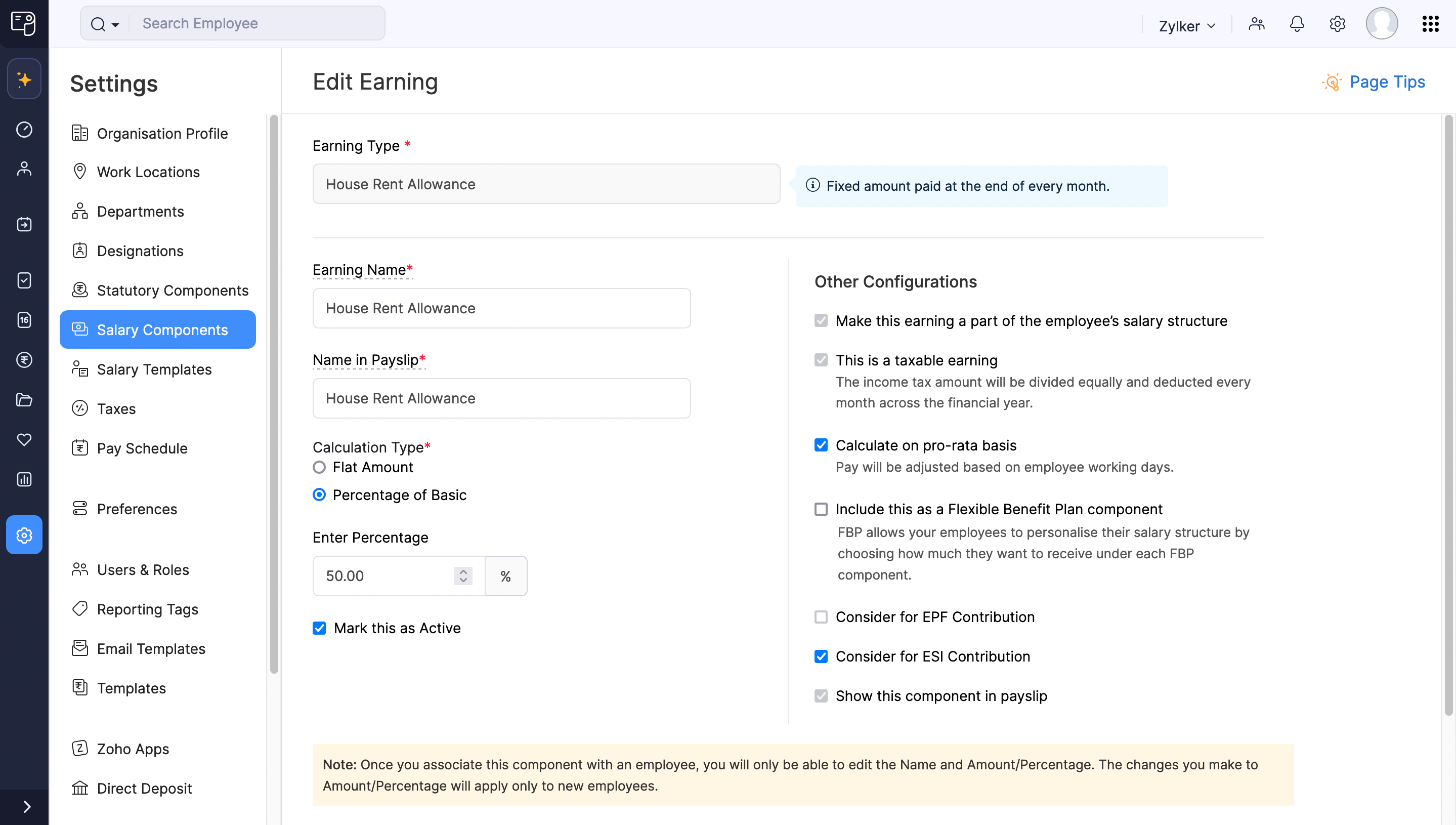
HRA calculation in Zoho Payroll
How to calculate HRA in salary?
1. HRA calculated as a percentage of basic salary
Suppose an employee named Rishi works in Mumbai and has a basic salary of ₹50,000 per month. His employer offers him an HRA equivalent to 27% of the basic salary. His HRA will be:
HRA = 27% of basic salary
HRA = ₹13,500 per month
2. HRA calculated as fixed amount
For HRA which is calculated as a fixed amount in CTC, the employer needs to mention it in the salary package of an employee. Here is a table showing the HRA amount in an employee’s CTC.
| Components | Amount (in ₹) |
| Basic salary | 40,000 |
| HRA | 23,000 |
| Conveyance allowance | 2,000 |
| Special allowance | 3,000 |
| Leave Travel Allowance | 5,000 |
| Gross salary | 73,000 |
Is HRA taxable?
The taxability of House Rent Allowance (HRA) depends on whether the employee lives in a rented house or not.
- For employees not living in rented accommodation: The full amount of HRA received is added to their net taxable income and taxed according to their applicable income tax slab.
- For employees living in rented accommodation: The entire HRA is not fully taxable. They can claim a tax exemption on HRA, which is governed by Section 10(13A) and Rule 2A of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
When calculating taxable income, the exempted HRA amount is deducted from the total income, which helps in reducing tax liabilities
What are the HRA tax exemption rules?
To claim HRA tax exemption, an employee must meet the following conditions:
- Employment status: The exemption is available only to salaried employees. Self-employed individuals are not eligible for HRA tax exemption.
- Rented accommodation: The employee must reside in a rented property and pay rent. Exemption is not available for those living in their own homes, as rent cannot be paid to oneself.
- Rent to relatives: If employees live in their parents' house and pay rent, they can still claim HRA exemption. To qualify for this exemption, the rent paid must be declared as income in the parent's income tax return.
- Informing the employer: Employees should inform their employer about the rent paid by submitting rent receipts. If the annual rent exceeds ₹1,00,000, the landlord’s PAN must be disclosed.
- Old tax regime requirement: HRA exemption is applicable only under the old tax regime. Employees opting for the new tax regime will not be able to claim this benefit.
- Claiming HRA in tax return: Even if HRA exemption is not reflected in Form 16, employees can claim it while filing their income tax return.
How to calculate HRA exemption?
The maximum HRA exemption an employee can claim under the Income Tax Act is the least of the following three amounts:
- Actual HRA received
This is the amount of HRA provided by you, the employer, as part of the employee's salary structure.
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of basic salary + dearness allowance
This amount is calculated by subtracting 10% of the employee's basic salary + dearness allowance from the actual rent paid.
- HRA limit based on city type
Metro cities: For employees residing in metro cities like Kolkata, Delhi, Mumbai, and Chennai, the maximum HRA exemption is 50% of their basic salary plus dearness allowance.
Non-metro cities: For those living in non-metro cities, the limit is lower, set at 40% of their basic salary plus DA.
You should calculate the exemption annually if the salary structure and rent amount remain constant throughout the financial year. If there are changes in salary or rent during the year, then you must calculate the exemption on a monthly basis.
HRA calculation in the old tax regime
Let’s consider Rahul, who works in Delhi and pays an annual rent of ₹1,68,000. His employer provides him with an HRA of ₹2,16,000. Below is an overview of his salary structure:
| Salary component | Annual amount (in ₹) |
| Basic salary | 3,00,000 |
| HRA | 2,16,000 |
| Conveyance allowance | 42,000 |
| Medical allowance | 18,000 |
| Special allowance | 30,000 |
| Gross salary | 6,06,000 |
To determine Rahul's HRA deduction, compare the actual rent paid by him with the following metrics.
| Particulars | Annual amount (in ₹) |
| Actual HRA offered by the employer | 2,16,000 |
| 50% of the basic salary (since Delhi is a metro city) | 1,50,000 (50% of ₹3,00,000) |
| Actual rent paid minus 10% of the basic salary | 1,38,000 [₹1,68,000 - (10% of ₹3,00,000)] |
The lowest amount among these options is ₹1,38,000. Therefore, Rahul is eligible for an HRA exemption of ₹1,38,000 on his total taxable income.
Pro tip: Use Zoho Payroll’s free HRA exemption calculator tool to easily calculate how much tax your employees need to pay on their HRA.
HRA calculation in the new tax regime
In the new tax regime, introduced in the FY 2020-21, claiming HRA exemption is no longer permitted. Consequently, the full HRA amount received from the employer is now included in taxable income.
For those who do not pay rent or have minimal rent expenses, the new tax regime may be advantageous, as it offers lower tax slabs without the need for HRA deductions. On the other hand, employees who pay substantial rent, particularly in metro cities, may face a higher tax liability due to the absence of HRA exemptions.
How to claim exemption on HRA?
To guide your employees in claiming HRA exemption during the time of filing ITR returns, follow these steps:
Step 1: Submit form 12BB
Ensure that employees submit an income declaration form (Form 12BB) to you. This form is essential for claiming HRA exemptions.
Step 2: Claiming during ITR filing
If employees forget or cannot provide the required details in Form 12BB, they can claim the exemption while filing their Income Tax Returns (ITR). Here is how they can do it:
- Calculate the eligible HRA exemption amount by identifying the lowest of the three calculations - actual HRA received, HRA limit based on city type and actual rent paid minus 10% of basic salary.
- Subtract the HRA exemption amount from the gross salary to calculate the taxable income.
- In the ITR form, employees need to enter the actual HRA received, the lowest of the three calculated amounts and the HRA exemption amount.
Step 3: Attach the necessary documents
Ensure that your employees attach essential documents such as rent receipts, rental agreements, and other relevant proofs of their rental status to support their HRA claim.
By following these steps, employees can effectively claim their HRA exemption during the ITR filing process.
HRA exemption for special cases
Here is how HRA exemption can be claimed for specific scenarios:
- Owning a house in a different city
Employees who own property in another city can still claim HRA for rented accommodation in their current city. They can also claim a home loan deduction for EMIs on their owned property. Both claims are covered under Section 10(13A) of the Income Tax Act with appropriate proof.
- Rent paid to family members
Employees can claim HRA for rent paid to family members, such as parents, if they provide a formal rental agreement, rent receipts, and bank transfer records. The employee or their spouse must not own the property.
- Rent shared with spouse
If rent is shared with a spouse, only one person can claim the full HRA deduction unless separate rent receipts are provided. Ensure no duplication to avoid tax issues.
- Employees without HRA from employer
Employees not receiving HRA from their employer can claim the benefit under Section 80GG of the Income Tax Act by filing Form 10BA.
Documents required to claim HRA exemption
To claim HRA exemption, employers should ensure employees provide the following documents:
- Rent receipts: It consists of the date, tenant's name, landlord's name, address of rental property, stay duration and a revenue stamp with the landlord's signature.
- Rental agreement: Obtain a photocopy of the rental agreement. For rent paid to family members, ensure similar documentation is provided, including bank statements for transaction proof.
- PAN card: If annual rent exceeds ₹1,00,000, collect the landlord's PAN details. If the landlord lacks a PAN card, they must provide a self-attested declaration.
HRA exemption claims best practices
As an employer, keep the following pointers in mind when processing HRA exemptions to ensure accurate salary calculations.
- Encourage timely submission of documents
Employers should remind employees to submit their rent receipts and supporting documents by the end of the financial year. This allows for accurate adjustments in tax deductions and ensures that the HRA exemption is properly reflected in Form 16 and their tax returns.
- Inform about additional requirements
Employees need to provide their landlord’s PAN if their annual rent exceeds ₹1 lakh. Ensure they are aware of this requirement to avoid issues with claiming HRA exemptions.
- Guide on filing without rent receipts
If employees miss the deadline for submitting rent receipts, let them know they can still claim the HRA exemption while filing their ITR. They should manually calculate the exempt amount and claim it in their ITR to correct any excess TDS deducted.
Conclusion
It’s clear that calculating HRA for each employee can be a complex and time-consuming task. But with Zoho Payroll, you can simplify this process.
Our payroll software automatically handles HRA calculations for you. Just input the employee’s CTC, and the software will break it down into different parts and make accurate tax deductions. This means less manual work for you and more time saved, making payroll management much easier.
Frequently asked questions on HRA
How much HRA can be claimed without proof?
Employees can claim HRA up to ₹3,000 per month without proof. For HRA amounts exceeding ₹3,000 per month, employees must submit rent receipts to qualify for the exemption.
How to calculate HRA in salary?
For HRA calculation, determine the lowest of the following three amounts:
- Actual HRA received from the employer.
- 50% of basic salary (for metro cities) or 40% (for non-metro cities).
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of basic salary + dearness allowance.
Under which income tax section does HRA fall?
HRA falls under Section 10(13A) of the Income Tax Act. This section governs the tax exemption on House Rent Allowance.
Which are the metro cities for claiming HRA deduction?
Chennai, Kolkata, Mumbai and Delhi are the metro cities for claiming HRA deductions.




