- HOME
- Payroll administration
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA): Exemption and calculation rules
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA): Exemption and calculation rules
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) is included in an employee’s Cost to Company (CTC) to cover the expenses incurred when they travel within the country for vacation purposes.
In this comprehensive guide, we will learn the meaning of LTA, its calculation, and exemption rules and how your employees can claim exemption on LTA.

LTA full form and meaning
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA), also known as Leave Travel Concession, is a type of allowance offered to employees in India. Employees who travel to any place within the country and meet the government's criteria can claim LTA from their employer.
This allowance covers travel expenses for leisure trips, making these costs tax-free for the employee.
Purpose of LTA
Employees can take a vacation and have their travel expenses exempt from taxes twice within a four-year block. LTA can be claimed only on actual travel expenses, excluding costs for sightseeing, local transportation, meals, hotel accommodations, or other related expenses.
To claim this benefit, employees must submit travel bills and documents, such as tickets, to their employer. The exemption applies solely to travel expenses and is subject to specific conditions.
Any unclaimed LTA in the salary can either be carried forward to the next year or encashed at the end of the financial year, depending on the company's pay structure.
Leave Travel Allowance calculation
An employer provides Leave Travel Allowance to an employee based on their job position, and this amount varies from company to company. To understand how LTA is calculated, let’s consider an example.
Suppose an employer offers an LTA of ₹35,000 to an employee. If the employee spends only ₹25,000 on travel, they will receive ₹25,000 from the employer. However, if the employee spends ₹40,000 on travel, they will still receive only ₹35,000, as that is the maximum LTA set by the employer.
Who can claim LTA?
To claim Leave Travel Allowance, employees need to meet specific criteria, which are as follows:
- Actual travel costs
Employees can claim LTA only for actual travel costs, whether by road, rail or air. They must provide valid proof of these expenses to claim the allowance.
Local conveyance, sightseeing, hotel stays, meals, and other non-travel expenses are not eligible for LTA.
- Domestic travel
Employees of a firm can claim LTA for domestic travel. It does not cover expenses from international trips.
- Claim frequency
Employees can claim LTA only for two journeys within a block of four years. These blocks are determined by the government. The current block is from the calendar years 2022-2025, with the previous block being 2018-2021.
- Leave from work
Employees must take leave from work specifically for travel purposes to claim LTA. Your employees must mark the period of travel as ‘leave’.
- Inclusion of family members
Employees can claim the exemption alone or with their family, which includes the spouse, children and wholly or mainly dependent parents and siblings.
- Block year
Employees are allowed to claim LTA twice in a block of 4 years. The remaining amount after 2 claims is usually carried forward to the next block year based on the company's pay structure.
LTA block year
The Government sets specific block years for Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) purposes. The concept of block years was introduced in 1986, with the first block being 1986-1989.
The current LTA block year is 2022-2025. It is important for employers to understand these block years to ensure that employees claim their LTA benefits within the designated period.
What are the conditions for claiming LTA?
To claim Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) exemption, employees must meet the following mandatory conditions:
- Valid proof of travel must be provided.
- The travel must be within India; international travel is not covered under LTA.
- LTA can be claimed by employees for themselves, their spouse, children, and dependent family members, such as parents and siblings.
- The exemption is allowed for a maximum of two children born after October 1, 1998. However, there are no restrictions for children born before this date or for multiple births after the first child.
Carryover of unclaimed LTA
If an employee has not claimed their LTA exemption for one or two journeys within a 4-year block, they can carry over one unclaimed exemption to the next block. However, an employee must use this in the first calendar year of the new block.
Is leave travel allowance taxable?
The amount claimed as Leave Travel Allowance is exempt from tax under the old tax regime if the conditions specified by the government are met.
However, for employees who opt for the new tax regime, the entire LTA amount will be fully taxable. Understanding these nuances is important to guide your employees in availing tax benefits applicable to them.
LTA exemption rules
The rules for LTA exemptions change based on the type of transport used. Here are the LTA exemption rules:
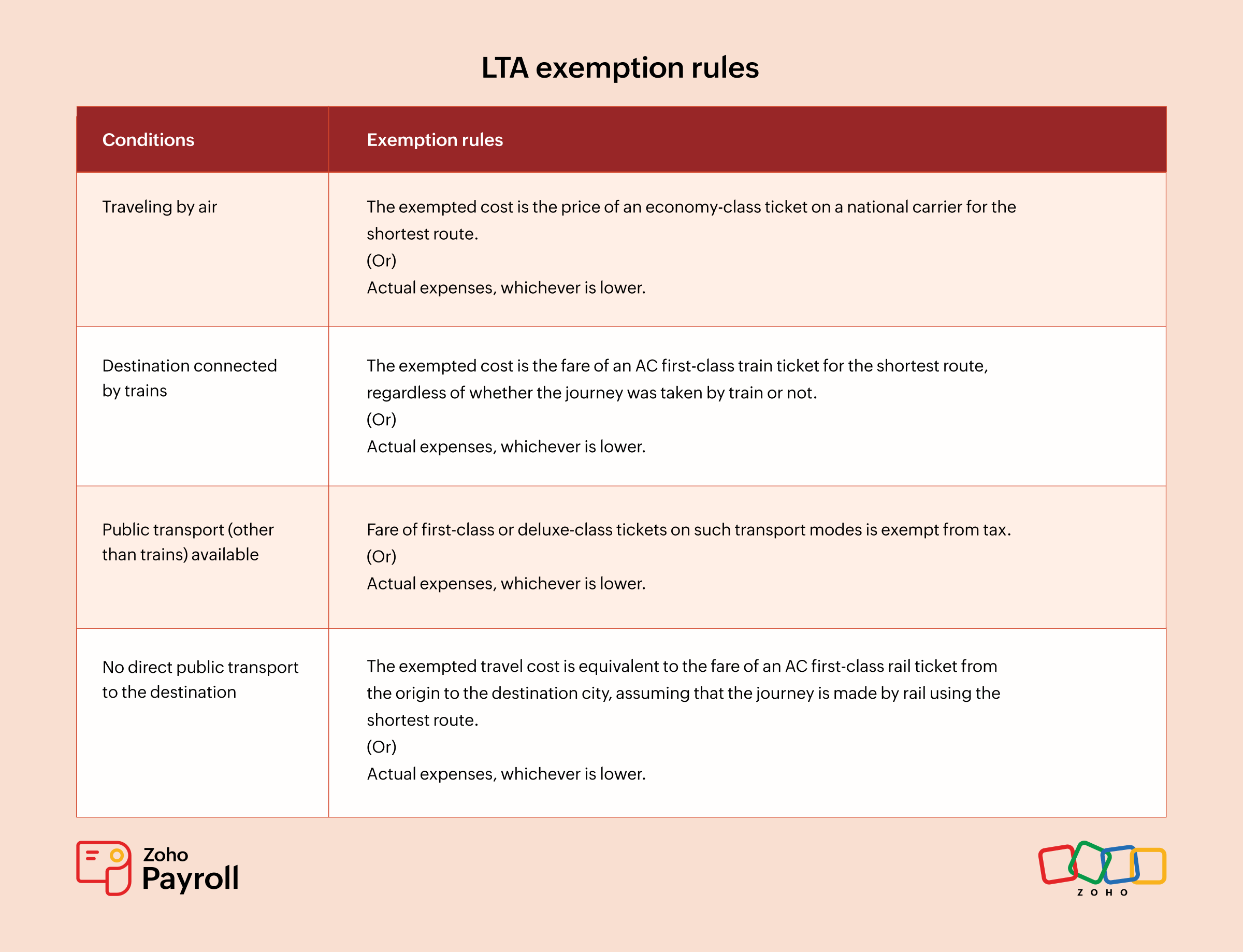
Benefits of leave travel allowance
LTA is a valuable part of the salary package that helps reduce taxable income. Here’s how it benefits employees:
- Employees can claim LTA for their personal travel fares or tickets within India.
- By submitting travel-related bills for journeys, employees can lower their taxable income.
- LTA can also cover travel expenses for family members such as parents, siblings, spouses and children, if they travel with the employee.
Key takeaways
LTA is a crucial component of an employee’s salary, offering valuable travel benefits. By understanding LTA rules, employers can optimize this benefit for their teams. To manage LTA and other benefits effortlessly, use Zoho Payroll.
The cloud-based payroll software simplifies payroll management, calculates salaries and deductions accurately, and ensures compliance with labour laws. Learn how Zoho Payroll can help you streamline payroll processes today!
Frequently asked questions on LTA
What is a leave travel allowance?
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) is a type of allowance provided by employers to employees in India, allowing them to claim tax exemptions on expenses incurred while traveling within the country. LTA covers travel costs for the employee and their family, such as airfare, train, or bus tickets, but excludes other expenses like accommodation, food, or sightseeing.
Can employees claim LTA for multiple trips in a year?
Yes, employees can claim LTA for up to two trips in a block of four calendar years.
What is the LTA exemption in the new tax regime?
As per the new tax regime, there is no LTA exemption applicable for employees for the financial year 2024-25.
Is there any difference between LTA and LTC?
LTA (Leave Travel Allowance) and LTC (Leave Travel Concession) essentially serve the same purpose but are used in different sectors. LTA is the term commonly used in the private sector, while LTC is used in the public sector. Both allowances help employees save on travel expenses and reduce their taxable income.




