- HOME
- Payroll administration
- Overtime allowance: Meaning, calculation formula, and rules
Overtime allowance: Meaning, calculation formula, and rules
As the business landscape becomes more competitive, companies are constantly seeking ways to stay ahead. One effective strategy is boosting workforce productivity, which can be achieved through overtime working hours. Overtime work means working for extended hours, and with it comes overtime allowance.
In this article, we will learn the meaning of overtime allowance, how overtime pay is calculated in an employee’s salary, its payment rules and more.
Overtime allowance meaning
Overtime refers to the extra hours worked by an employee beyond their regular working hours. If an employee works more than the usual hours in a day or week, the employer must pay them overtime allowance for the additional time worked.
For example, if the standard workweek is 40 hours and an employee works 45 hours, they must be paid an overtime allowance for those extra 5 hours.
The main purpose of overtime allowance is to ensure that employees are fairly compensated for the extra hours they put in. This overtime pay rate can vary based on the company and the nature of the work.
What the labour laws say about overtime allowances
In India, several laws govern overtime payments and eligibility criteria for employees. Here's a summary of these regulations:
| Labour law | Overtime regulations |
| Minimum Wages Act, 1948 | If an employee's minimum wage is set by the hour, day, or any longer period under this Act, and they work more hours than a normal working day, the employer must pay them for each extra hour worked at the overtime rate. |
| Factories Act, 1948 | Overtime pay must be twice the regular wages and overtime hours should not exceed 10 hours a day, with mandatory breaks after 4 to 5 hours of work. |
| Plantation Labour Act, 1951 | Workers cannot work in plantations more than 54 hours a week, including overtime. Overtime pay must be double the regular pay. |
| The Mines Act, 1952 | If a person works in a mine for more than 9 hours above ground, more than 8 hours below ground in a day, or over 48 hours in a week, they are entitled to overtime pay. This overtime pay must be double their regular wage. |
| Contract Labour (Regulation & Abolition) Act, 1970 | Contractors must maintain an overtime register containing details of workers' overtime hours, work timings, dates and employee names. |
Overtime as per the Factories Act
As per Section 59 of the Factories Act of 1948, employees who work for more than 9 hours in a day (or 48 hours in a week), should receive double their normal wages for the extra hours worked.
Here the normal wage refers to the basic wages an employee receives along with allowances and excludes bonuses and extra wages for working overtime.
When calculating overtime pay, the company will use the worker's average daily earnings in the month before the overtime was worked. If the worker didn't do the same job in the previous month, their overtime pay will be based on their average daily earnings from the week when the overtime was worked.
Overtime allowance calculation formula in India
The standard working hours in most industries are 8 hours a day or 48 hours a week. If employees work beyond these hours, they are entitled to overtime pay. Here's how overtime pay is calculated in India:
Overtime allowance = Normal hourly wages * 2 * overtime hours worked
- Normal hourly wages: The employee’s hourly wage rate, which is calculated based on their daily or monthly wage.
- Overtime hours worked: The total number of hours an employee has worked beyond the regular working hours.
How to calculate hourly wage
To calculate the hourly wage, you first need to determine the daily wage and then break it down into an hourly rate.
Typically, there are 26 working days in a month (assuming 4 Sundays off) and 8 working hours per day. Let’s take an example to illustrate how hourly wage and overtime is calculated.
Example of overtime calculation
Assume you have an employee who earns ₹30,000 (basic salary + allowances) every month. Their regular working hours are 8 hours a day. Their daily and hourly wages are calculated as follows:
- Daily wage = Monthly salary/ Number of working days = 30,000/26 = ₹1,153
- Hourly wage = Daily wage/ Working hours per day = 1,153/8 = ₹144
Suppose the employee worked 10 hours on a specific day. The overtime allowance to be paid to them will be:
Overtime allowance = Normal hourly wages * 2 * overtime hours worked
Overtime pay = ₹144 * 2 * 2
Overtime pay = ₹576
The employee would receive ₹576 as overtime allowance for working 2 extra hours on that day.
Note: If the employee works overtime across several days, the monthly overtime pay would be the sum of overtime allowances for all extra hours worked.
Overtime payment rules
Overtime allowance is typically calculated on a monthly basis and added to the employee’s gross salary.
Employers in India are legally required to maintain records of the overtime hours worked in an overtime register or attendance system. Based on these records, the overtime payment is calculated and paid at a rate that is generally twice the regular hourly wage.
The amount received as overtime pay is considered part of the employee's taxable income and is fully subject to income tax. The overtime pay must be mentioned on the employee’s salary slip to ensure payroll transparency and avoid potential discrepancies.
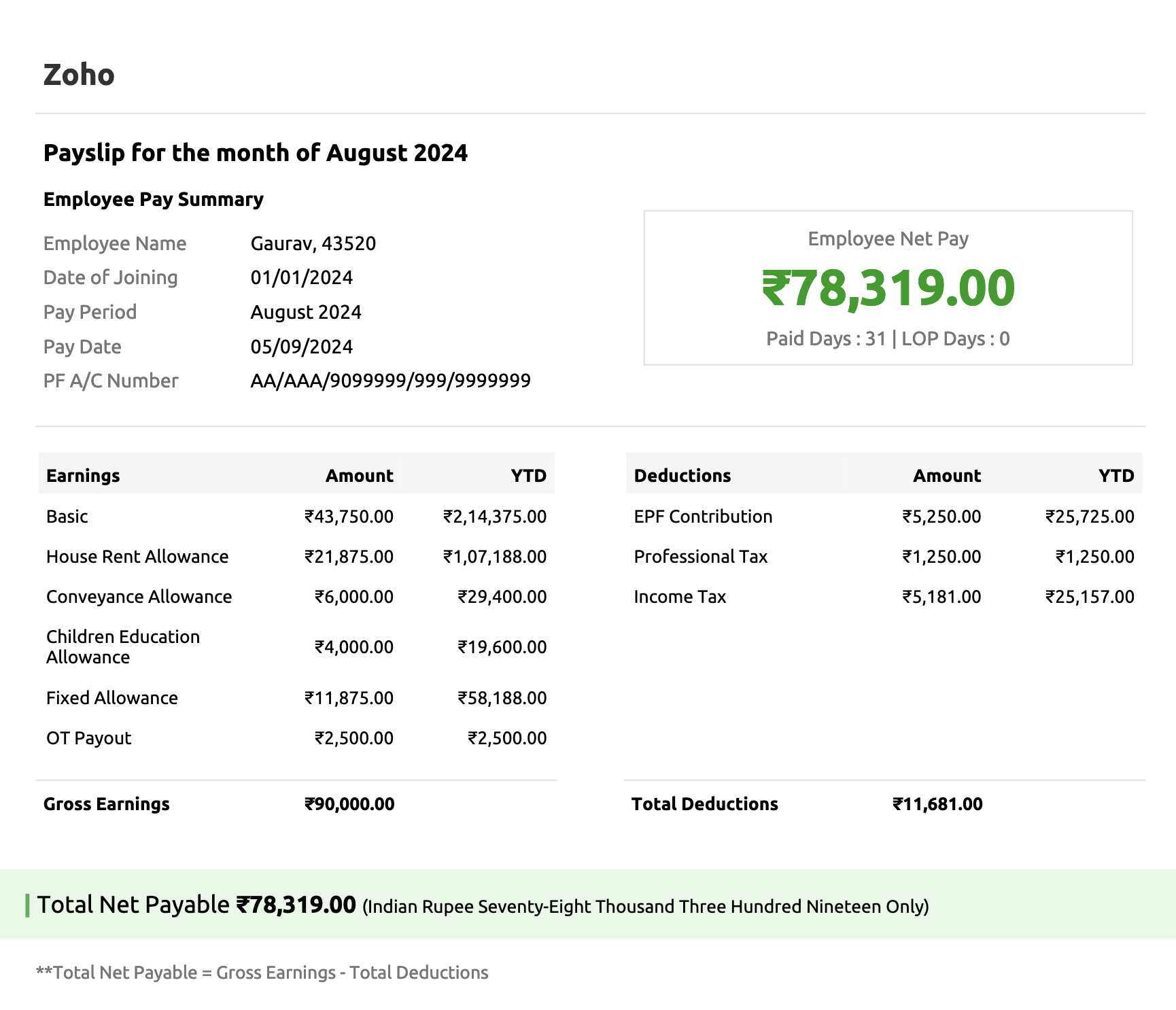
Sample salary slip with overtime allowance generated by payroll software–Zoho Payroll.
Overtime register for workers
Employers should maintain a register to track the overtime hours worked by employees. This register is crucial for calculating overtime pay accurately. This document must contain the following details:
- Employee’s name and gender
- Designation and department
- Employee’s and the organisation’s normal working hours
- Gross salary and hourly wages of the employee
- Total overtime hours worked on a specific day
- Overtime rate (calculated based on the number of hours worked by an employee that exceed those defined for a standard workweek)
- Overtime earnings (amount payable or paid to employees for overtime hours during the entire payroll month)
- Date on which overtime payments are made
Here is the overtime register form that you can make use of for your workers:
https://labour.and.nic.in/labour/registerFormats/OTRegsiter.pdf
Company overtime policy
Designing a comprehensive overtime policy will help you manage labour costs by controlling the expenses associated with employees who work extra hours to meet deadlines. Ensure your policy fairly compensates employees for the additional hours they put in while also aligning with the regulations set by the central and state governments.
For example, during busy periods, you may need your team to work overtime to complete time-critical projects. At the same time, you must ensure compliance with labour laws and provide employees with all legally required benefits.
Key takeaways
Employers must establish clear and transparent overtime allowance policies to ensure fairness and compliance with labour laws. Regularly reviewing and updating overtime records is essential for maintaining accuracy.
For streamlined payroll management and compliance with overtime regulations, employers should switch to Zoho Payroll, a cloud-based payroll software that ensures accurate processing of overtime allowances and all other salary components. Automate your payroll calculations today and keep your business on solid legal footing with Zoho Payroll.
Frequently asked questions on overtime
What is overtime in work?
Overtime in work refers to the additional hours an employee works beyond their standard working hours. This extra time is compensated at a higher rate than regular hours. When an employee exceeds their usual working schedule, it qualifies as overtime.
What do the new labour codes say about overtime pay?
Under the new labour codes, the central or state governments will set the standard working hours. If employees work overtime, they receive overtime payment, which must be at least double their regular wages.




