What is Weighted Average Costing (WAC) method in Zoho Inventory?
Weighted Average Costing (WAC) is an inventory valuation method that calculates the average cost of all inventory items. This average cost is then used to determine the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and the value of your remaining stock .
Here’s How the Weighted Average Cost Is Calculated (WAC):
The Weighted Average Cost (WAC) method calculates the total value of available quantities and divides it by the total quantity available.
In simple terms,

Let’s break it down with an example,
1. Initial Transaction:
| Transaction | Quantity | Unit Price (BCY) |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase | 1 | 10 |
| Purchase | 2 | 20 |
2. Weighted Average Costing (WAC) Calculation:
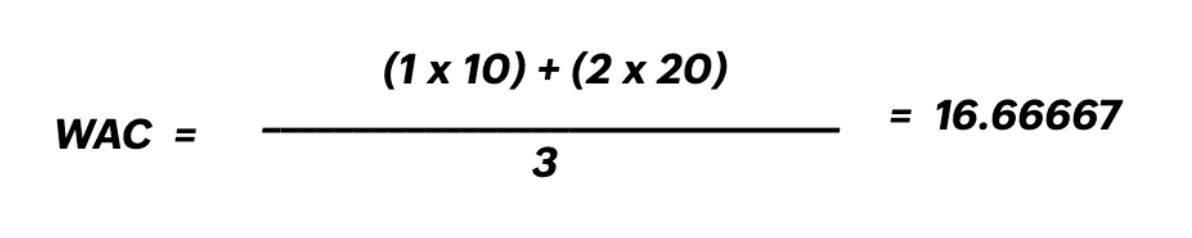
This means every unit of stock is now valued at 16.67.
3. Sales Transaction
| Transaction | Quantity Sold | Weighted Average Costing (WAC) | Remaining Stock | Remaining Value (BCY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | 1 | 16.6667 | 2 | 33.34 |
Here’s How the Weighted Average Costing (WAC) Is Then Updated:
With Moving Average Costing/Perpetual Average, the WAC is recalculated every time you add new stock. Here’s an example of how this works:
1. New Transactions
| Transaction | Quantity | Unit Price (BCY) |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase | 1 | 5 |
2. Updated WAC:
Here’s how we can calculate the updated Weighted Average Costing:
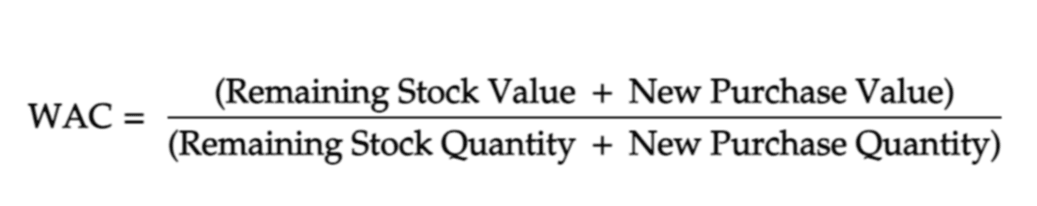
Applying this formula, we get:
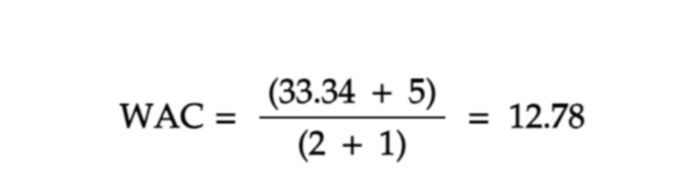
3. Sale after update:
| Transaction | Quantity Sold | Weighted Average Costing (WAC) | Remaining Stock | Remaining Value (BCY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | 1 | 12.78 | 2 | 25.56 |
Use Cases
Let’s take a look at some of the other use cases for WAC:
Negative Inventory
Use Case: You record a sales transaction before purchase, causing inventory to temporarily go negative. This can happen if stock is sold before it’s recorded in the system.
Example:
| Date | Transaction | Quantity | Unit Price (BCY) | Stock Level | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan 5 | Sale | -1 | ??? | -1 | Negative inventory created |
| Jan 7 | Purchase | +2 | 20 | 1 | Stock added |
WAC after purchase:
- Total cost = 2 × 20 = 40
- Total quantity = 2 (even though 1 was already sold, it is now fulfilled)
- WAC = 20
- Backdated sale on Jan 5 will use this updated WAC
Half Inventory
Use Case: Customer demands more stock than is available. Only part of the order can be fulfilled. Common in bulk or raw material industries.
| Date | Transaction | Quantity | Unit Price (BCY) | Stock Level | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feb 1 | Purchase | 5 | 30 | 5 | Initial purchase |
| Feb 2 | Sale (Attempted: 10) | 5 | 30 (WAC) | -5 | Only 5 units sold due to limited stock |
- Requested Sale Order Quantity: 10 units
- Available Stock: 5 units
- WAC = 30 (remains the same until new purchase)
- Sale is partially fulfilled with available stock. Remaining 5 units are pending or backordered.
Zero Inventory (WAC Reset)
Scenario: Stock is completely sold out. When a new purchase arrives, a fresh WAC is calculated (previous WAC is discarded).
| Date | Transaction | Quantity | Unit Price (BCY) | Stock Level | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mar 1 | Purchase | 3 | 15 | 3 | Initial purchase |
| Mar 3 | Sale | 3 | 15 (WAC) | 0 | Inventory exhausted |
| Mar 5 | Purchase | 4 | 20 | 4 | WAC resets to 20 (new cost) |
- WAC before Mar 3 Sale: 15
- Inventory after sale: 0
- Mar 5 Purchase: WAC becomes 20 (based solely on new purchase)
- No carry-forward of previous WAC when inventory is zero
Backdated Transaction
Use Case: You add or edit a transaction with a backdated entry. This can affect historical WAC and COGS if the system recalculates retroactively.
Example:
| Date | Transaction | Quantity | Unit Price (BCY) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apr 5 | Sale | 1 | ??? | WAC unknown if no purchase yet |
| Apr 7 | Purchase | 2 | 25 | WAC = 25 (recorded later) |
| Apr 3 | Purchase(backdated) | 1 | 20 | New WAC = (20 + 50) / 3 = 23.33 |
The April 5 sale now uses WAC = 23.33 instead of 25.


