- HOME
- HR insights
- Equal employment opportunity (EEO): A comprehensive guide for employers and employees
Equal employment opportunity (EEO): A comprehensive guide for employers and employees
- Last Updated : January 8, 2026
- 1.3K Views
- 5 Min Read

Creating a fair and inclusive work environment is not just a moral imperative, it's the law. Equal employment opportunity (EEO) is a set of principles ensuring everyone gets a shot at landing their dream job based on merit, not background. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore more about EEO, it's importance, who files it and how, where to file, and the penalties for non-compliance. If you're an employer aiming to understand how to comply with federal laws, or an employee who wants to understand their rights, this post is for you. Let's dive in!
What is equal employment opportunity?
Equal employment opportunity, or EEO, defines equality in workplace. This means all the individuals working in an organization have equal opportunity in terms of jobs, promotions, training, and much more based on their skills and qualifications, regardless of factors like race, color, religion, national orientation, gender, age, disability, or sexual orientation. This is enshrined in several federal laws aimed at ensuring a fair and inclusive workplace for all employees and job applicants. The goal is to create a level playing field where everyone gets a fair chance to compete.
Importance of equal employment opportunity
EEO is essential for fostering a diverse and inclusive workplace where all employees can thrive. It helps to prevent racially discriminatory practices, promotes equal treatment, and ensures that hiring, promotions, and other employment decisions are made based on qualifications and performance rather than biases or prejudices.
Key equal employment opportunity laws
Several federal laws support EEO, including:
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967 (ADEA)
The Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA)
The Genetic Information Non-discrimination Act of 2008 (GINA)
The Equal Pay Act of 1963 (EPA)
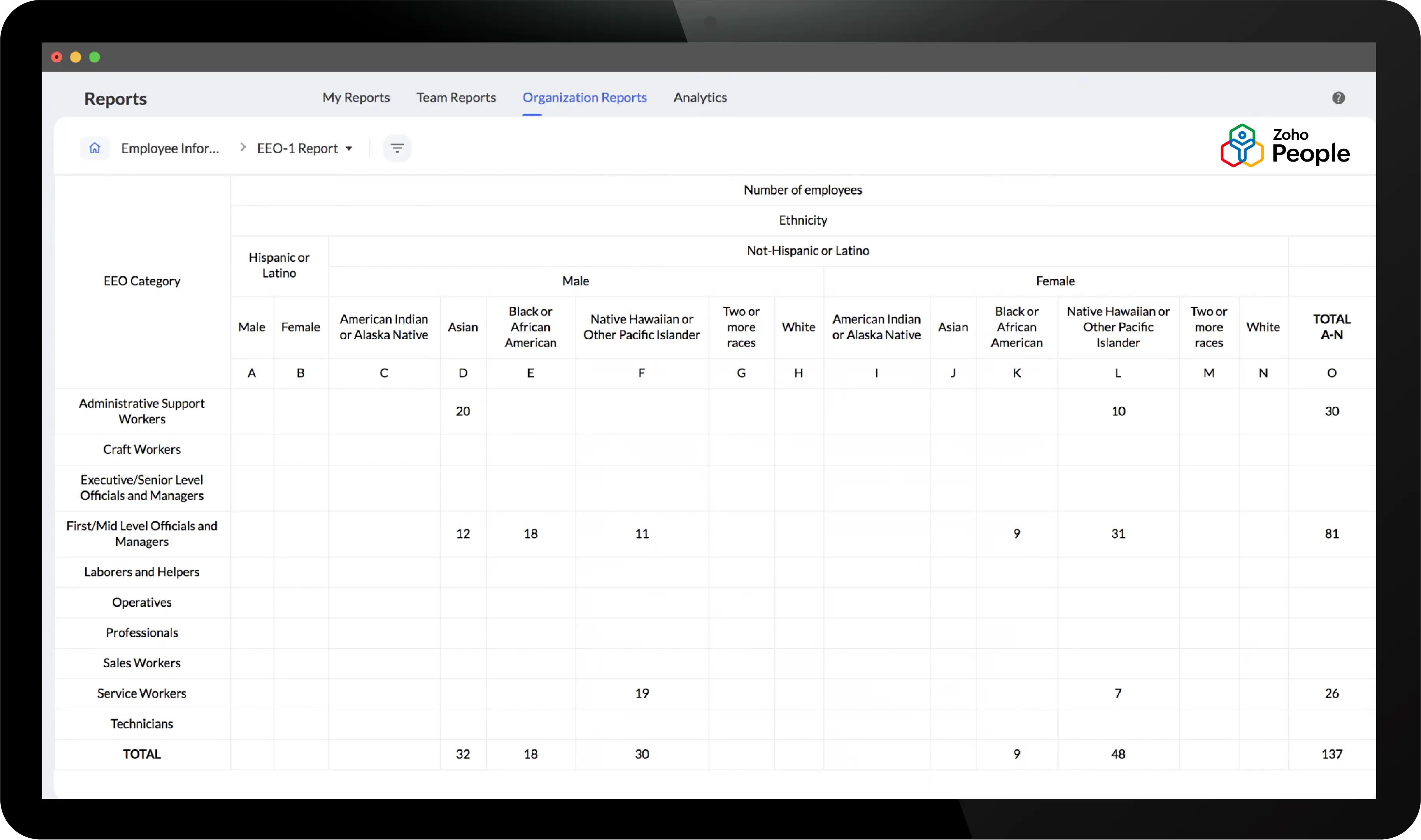
Filing an EEO-1 report (for employers)
To ensure compliance with EEO laws, employers needs to file an Employer Information Report. This is also known as the EEO-1 Component 1 report or the Standard Form 100, and it's a mandatory data collection report submitted annually by employers to the US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). This report is used to identify the number of employees working in the organization, along with their race, ethnicity, and gender.
Who needs to file an EEO-1 report?
Private organizations with 100+ employees.
Federal contractors and first-tier subcontractors with 50+ employees and a contract of $50,000 or more with the federal government.
When should employers file an EEO-1 report?
Generally, the deadline to file the EEO-1 report is March 31, but the deadline may vary.
For the 2023 EEO-1 Component 1, the data collection was opened on April 30, 2024. Employers must submit the EEO-1 report to the EEOC on or before July 9, 2024.
What information is required to file an EEO-1 report?
To file an EEO-1 report, employers need the following information:
Name and address of the parent company
Employment data, such as:
Number of employees based on job categories, from executive/senior level officials to service workers
Number of employees based on race/ethnicity
Number of employees based on gender
Certification
Name, title, and signature of the certifying official
- Name, title, email, and address of the contact person
How to handle transgender reporting for the EEO-1 form?
In the EEO-1 form, there is a category for gender, but it only includes male and female; there is no transgender option. In this case, employers are asked to report the gender based on the employee's gender identity rather than choosing the biological sex. This is done to reduce discrimination against transgender employees.
How to file an EEO-1 report?
Employers can file an EEO-1 report electronically using the online portal provided by the EEOC.
Step 1: Log in to the EEOC online portal. (Sign up if you are a first time user.)
Step 2: Enter all the required data.
Step 3: Review all the data and submit it.
Step 4: Track changes in EEO-1 reporting requirements.
For detailed information on how to file an EEO-1 report through the online portal, check out the instruction booklet on the EEOC website.
Note: If you are using Zoho People, the EEO-1 report is only enabled for US-based accounts (both for existing and new customers). If your account is based in another region but has employees in the US, the report can be enabled on request. Please contact support@zohopeople.com for assistance.
Penalties for non-compliance in EEO-1 reporting
Providing false information or failing to file the EEO-1 form on time will lead to a significant penalty. Penalties may include:
Monetary fines
Legal action by the EEOC
Order to file by a U.S. District Court
Potential loss of federal contracts for government contractors
For detailed information on EEO-1 reporting, click here.
Filing an EEO complaint (for employees)
Employees can file an EEO complaint with the EEOC if they feel discriminated against in the workplace. This includes situations where promotions or raises are given to someone less qualified from a different background, being laid off while seemingly less qualified colleagues remain, or facing a hostile work environment due to the employee's identity.
When and where to file an EEO complaint?
Employees need to register their complaint with the EEOC on or before the 180 days from the date of discrimination. Employees have 300 days if the discrimination involves a federal agency. Complaints can be filed online at https://www.eeoc.gov/ or by calling 1-800-669-4000.
More on how to file an employment discrimination charge.
What happens after filing an EEO complaint?
The EEOC will investigate the employee's complaint to determine if there's reasonable cause to believe discrimination occurred by reviewing documents, interviewing witnesses, and gathering evidence. If they find merit to the claim, they'll attempt to mediate a settlement between the employee and the employer. If that fails, employees may have the right to sue in court.
Penalties for violation of EEO by employers
Employers must ensure their recruitment, hiring, promotion, and termination practices are fair and unbiased. Violating EEO laws can be costly. Employers found guilty of discrimination may be ordered to provide compensation to the affected employee, reinstate them to their position, and even face civil penalties.
Promoting EEO in the workplace
Beyond legal compliance, promoting EEO in the workplace involves creating policies and practices that encourage diversity and inclusion. This can include:
- Implementing anti-discrimination training programs
Establishing clear policies against harassment and discrimination
Providing reasonable accommodations for employees with disabilities
Promoting a culture of respect and inclusion
Wrapping up
Equal employment opportunity is a cornerstone of a fair and just workplace. By understanding its principles and procedures, both employees and employers can work together to create a level playing field where everyone has the chance to thrive. So, let's commit to EEO and build workplaces that value diversity, inclusion, and opportunity for all!


